AIR QUALITY
On this information page you will find everything about air quality, its components, pollutants present in it and how it can be treated by means of ionization.
WHAT IS AIR?
Air quality is the degree of purity of air, which mainly refers to impurities.
“Clean air” is defined as a mixture of gases consisting of:
Nitrogen (78.08%), Oxygen (20.95%), Argon (0.93%) and traces of various other gases.
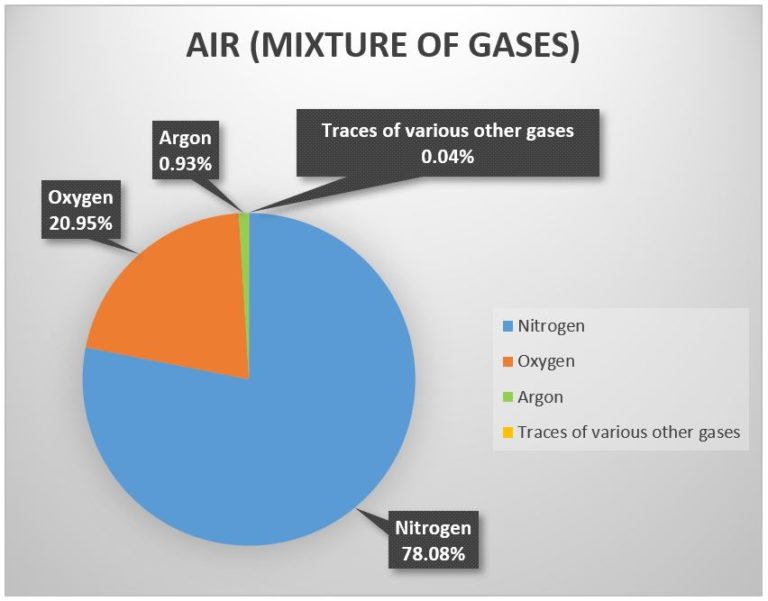
Picture 1
Due to industrialization, advancing technologies, fossil fuel transportation and other human inventions, chemical substances are continuously emitted, transformed and released into indoor or outdoor air (via chimneys, exhaust gases, used breathing air, etc.).
As a result, the air quality is constantly changing, as foreign substances are added which can be harmful to humans, animals and nature, and in large concentrations can even be fatal in the long term.
PERCEPTION
Pollutants can only be perceived by the human senses to a limited extent. However, the best organ for this is most likely the nose.
The term for measuring the response of odorous perception to odorant concentrations is “olfactometry”.
Odors of natural origin such as organic waste, fecal or decomposition odors are well known to most people.
However, odors from chemical processes, so-called “volatile organic compounds” (VOCs), can also be harmful gases that attack the mucous membranes, cause irritation of the respiratory tract and eyes, or even promote long-term damage when absorbed into the body.

Picture 2
What can be said with certainty on this topic is that odors are perceived subjectively. What one person finds pleasant, another person will classify as smelly. This sometimes depends on various factors such as: Odorant, odor concentration and even personal inclinations and memories/experiences. For example, the smell of freshly baked cookies may make one think of one’s carefree childhood in grandmother’s kitchen, while the smell of Tilsiter cheese is more reminiscent of unwashed feet.
SAFETY

Picture 3
Nature has found a wonderful solution for air purification. Forests, flowing waters and thunderstorms create ozone, as well as oxygen ions, which combine with pollutants (viruses, bacteria and odor molecules) and decompose or neutralize them. This is why the air in such areas or after a thunderstorm smells so fresh, as the ion content is quite high. This natural process is reproduced electrically with the ionization technology.
Find out more in our Technology section.
Since ozone is generally classified as a harmful gas, guideline values for the maximum workplace concentration (MAK value) are specified by the health authorities in all countries.
This value is 0.1 ppm or 0.2 mg/m³ in Switzerland and Germany.
These guide values also apply to all ionizing units and must be demonstrably complied with in individual operation, as specified in “DIN EN 60335-2-65”.
Since all our units are built according to these standards, they are absolutely safe and have been used for decades in many everyday areas and places around the world. We often say, “Odors occur everywhere life is created, to where life ends”. So, since odors and other pollutants are found almost everywhere, the field of application is also so versatile.
In the case of air ionization systems (several units coupled together and controlled), in practice the setpoint is calculated individually according to the room volume in m³ and the air exchange rate in m³/h, so that the MAK value cannot be exceeded even at full capacity. This requires some know-how and expertise and should therefore be determined and designed by a specialist.
DIFFERENCE OZONE TO OXYGEN IONS
This is probably the most frequently asked question from our customers as soon as they have looked into ionization technology. Because many sources of information talk exclusively about ozone.
The measurement of the oxidation value in the air, popularly called “ozone value”, is a summary measurement of the ozone concentration as well as oxygen ions in order to be able to determine a common limit value in the air. However, it is important to distinguish between these two.
Unfortunately, the ozone value has repeatedly led to confusion of ozone with oxygen ions, as has the fact that the odor of oxygen ions resembles the odor of ozone at sufficiently high concentrations.
OZONE MOLECULES
Ozone is that oxygen which is called O³ by the chemist. This O³ reacts spontaneously and aggressively. Inhaling ozone in higher concentrations (>0.1 ppm) over a longer period of time is therefore harmful. However, this naturally occurring gas is one of the most important trace gases in our atmosphere, as it protects us from ultraviolet radiation (keyword: ozone layer).
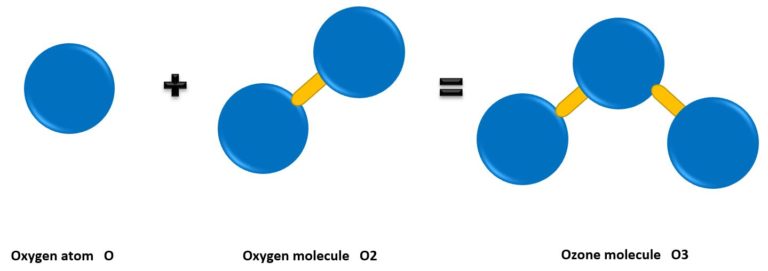
Picture 4
Oxygen atoms form a compound to ozone with a very high energy supply (>3kV). In return, the half-life (time until this compound dissolves again) is only a few hours.
OXYGEN IONS
An easier way to illustrate what an ion is is with the following image:
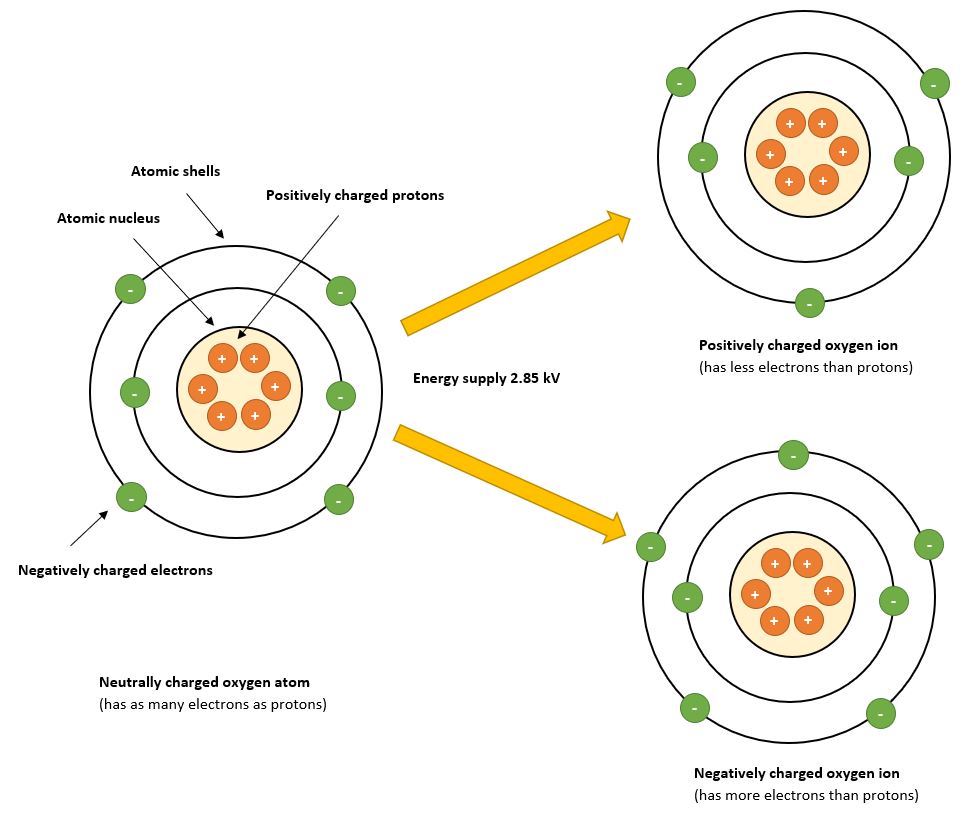
Picture 5
Especially the negatively charged oxygen ions are of crucial importance for the purification process of the air. Therefore, also predominantly negatively charged particles are generated by our ionization tubes.
OXYGEN CLUSTERS
“When the energy supply is applied just below 3kV, relatively diffuse electron emissions and enormous amounts of charged O2 molecules are produced, which attach to each other as a result of their charge potential. Oxygen clusters are formed, i.e. molecular clusters of about 10-60 O2 molecules. According to this, ozone is not O3, as was erroneously assumed in the past. This was proved by Prof. Dr. Tschischewsky in 1937 in the Institute for Air Ionization in Moscow.” (*¹)
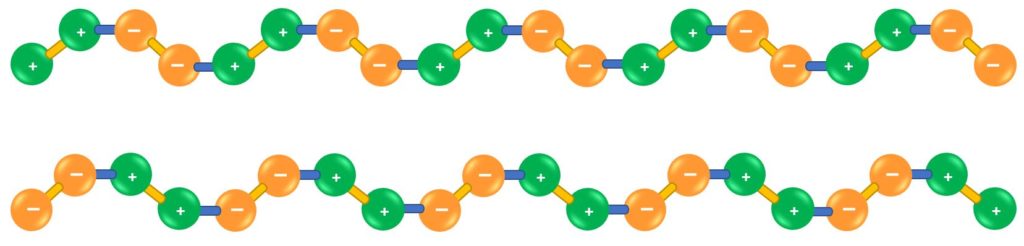
Picture 6
These oxygen ions react slower and milder in the air than ozone, so that they are well tolerated by living beings and still have the same positive properties against pollutants as ozone.
Good to know: Because of the smaller charge potential of the ion, energy is extracted from a neighboring O3 ozone molecule. This actually reduces the energy content of ozone in space and accelerates its decomposition.
SUMMARY
In conclusion, several points can be summarized:
- Oxygen ions are not ozone
- All equipment offered by us and systems designed by us comply with the safety standards applicable
- Smells are perceived differently by everyone and are subjective
- By using ionization, the indoor & outdoor air can be purified so that good air quality is restored
SOURCE LIST
TEXT SOURCES
(*1) – Special print «Die strahlungsfreie Hospitaldesinfektion» of C. J. Habicht, Director, Bentax AG, Publication date: 1980, of «media», No. 6/80, Swiss trade journal for medical technology, medical and hospital supplies
MEDIA SOURCES
Picture 1 – Title: Pie chart Air – Mixture of gases, Air-O-Clean AG, 31.07.2023
Picture 2 – Title: dog-838281_1280.jpg, Photographer: „LUM3N“, pixabay.com, 31.07.2023
Picture 3 – Title: rubber-stamp-gde91805a8_1280.png, Photographer: „Stampf“, pixabay.com, 03.08.2023
Picture 4 – Title: Ozone molecule, Air-O-Clean AG, 31.07.2023
Picture 5 – Title: Oxygen ion, Air-O-Clean AG, 31.07.2023
Picture 6 – Title: Sauerstoff / Oxygen cluster, Air-O-Clean AG, 31.07.2023
